The Atlantic has served as a favorite, well-travelled route for the pioneer who cast his eyes westward. For numerous reasons, some more obvious than others, Canada and the United States have attracted their share with Canada alone settling over three million newcomers in the years 1896-1914. In 1906, Lord Strathacona, formerly Donald Smith of the CPR, predicted a population of at least 80 million by the end of the twentieth century – the century Prime Minister Sir Wilfred Laurier boasted belonged to Canada. It was a time of optimism.
Prior to the wave of newcomers associated with the Laurier years, 1896-1911, the Silverman’s of Poland traversed the Atlantic, landing in New York. Three brothers – Aaron, Myer and Miram – soon would reach Algoma district and make Sudbury their home.
Aaron Silverman had been in his early teens when he arrived in New York. Employment in a clothing factory terminated when the factory closed. Soon he would be in Algoma district.
























 My Dad was a Cree Indian. He was raised to be self sufficient in the bush. He was raised to know the importance of providing for his family through hard work and dedication. He was, in the true sense of the phrase, a hunter and a gatherer. Dad was not an educated man in the sense of a formal education. He went as far as grade three and realized that he could do more for his family by working at a logging camp at the age of twelve. He did a variety of jobs but always remained close to his cultural roots and continued to hunt, trap and fish to supplement his meager wages.
My Dad was a Cree Indian. He was raised to be self sufficient in the bush. He was raised to know the importance of providing for his family through hard work and dedication. He was, in the true sense of the phrase, a hunter and a gatherer. Dad was not an educated man in the sense of a formal education. He went as far as grade three and realized that he could do more for his family by working at a logging camp at the age of twelve. He did a variety of jobs but always remained close to his cultural roots and continued to hunt, trap and fish to supplement his meager wages. Faults and Fissures Vein Deposits
Faults and Fissures Vein Deposits
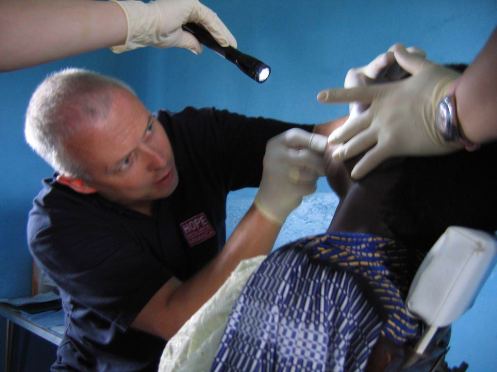 Over 5,000 villagers living in Tanzania’s Lake Victoria area have received free emergency dental care, thanks to a unique partnership Barrick established with Bridge2Aid in 2003. Bridge2Aid is a British NGO specializing in providing dental care in Tanzania, where experts estimate 70 to 90 per cent of the population have no access to dental care.
Over 5,000 villagers living in Tanzania’s Lake Victoria area have received free emergency dental care, thanks to a unique partnership Barrick established with Bridge2Aid in 2003. Bridge2Aid is a British NGO specializing in providing dental care in Tanzania, where experts estimate 70 to 90 per cent of the population have no access to dental care.  Imagine yourself in Grade 12 again. What do you remember? Did part of your schooling include visiting an underground mine and witnessing the various career opportunities available there? Do you remember receiving certification awareness training at a local employer, alongside other workers in the plant? Upon graduation, were you able to say that you had the skills and knowledge to pursue your postsecondary destination of choice, had spent time shadowing the types of jobs you were interested in, and had acquired a number of certifications that made you more appealing to employers?
Imagine yourself in Grade 12 again. What do you remember? Did part of your schooling include visiting an underground mine and witnessing the various career opportunities available there? Do you remember receiving certification awareness training at a local employer, alongside other workers in the plant? Upon graduation, were you able to say that you had the skills and knowledge to pursue your postsecondary destination of choice, had spent time shadowing the types of jobs you were interested in, and had acquired a number of certifications that made you more appealing to employers? John Campbell Miles (1883 – 1965) was the prospector and pastoral worker who discovered the mineralisation upon which the famous Mt Isa Mine was established in Queensland.
John Campbell Miles (1883 – 1965) was the prospector and pastoral worker who discovered the mineralisation upon which the famous Mt Isa Mine was established in Queensland. Patrick (Paddy) Hannan (1843 – 1925) was one of the prospectors whose discovery of gold in 1893 paved the way to mining in Kalgoorlie-Boulder, Western Australia.
Patrick (Paddy) Hannan (1843 – 1925) was one of the prospectors whose discovery of gold in 1893 paved the way to mining in Kalgoorlie-Boulder, Western Australia.