This column was published in the March 17, 2011 issue of Northern Life.
Stan Sudol is a Toronto-based communications consultant who writes extensively on mining issues. stan.sudol@republicofmining.com
For an extensive list of articles on this mineral discovery, please go to: Ontario’s Ring of Fire Mineral Discovery
“In the next 25 years, demand for metals could meet or exceed what we have used
since the beginning of the industrial revolution. By way of illustration, China needs to
build three cities larger than Sydney or Toronto every year until 2030 to accommodate
rural to urban growth.” (John McGagh, Rio Tinto – Head of Innovation)
Commodity Super Cycle is Back
The commodity super cycle is back, and with a vengeance. China, India, Brazil, Indonesia and many other developing economies are continuing their rapid pace of industrialization and urbanization. In 2010, China overtook Japan to become the world’s second largest economy and surpassed the United States to become the biggest producer of cars.
During a recent speech in Calgary, Mark Carney, the Governor of the Bank of Canada remarked, “Commodity markets are in the midst of a supercycle. …Rapid urbanization underpins this growth. Since 1990, the number of people living in cities in China and India has risen by nearly 500 million, the equivalent of housing the entire population of Canada 15 times over. …Even though history teaches that all booms are finite, this one could go on for some time.”
At the annual economics conference in Davos, Switzerland, held last January – where the most respected world leaders in politics, economics and academia gather – the consensus was one of enormous global prosperity predicting that, “For only the third time since the Industrial Revolution, the world may be entering a long-term growth cycle that will lift all economies simultaneously…”
John McGagh, head of innovation, at Rio Tinto – the world’s third largest mining company – has said, “In the next 25 years, demand for metals could meet or exceed what we have used since the beginning of the industrial revolution. By way of illustration, China needs to build three cities larger than Sydney or Toronto every year until 2030 to accommodate rural to urban growth. This equates to the largest migration of population from rural to urban living in the history of mankind.”
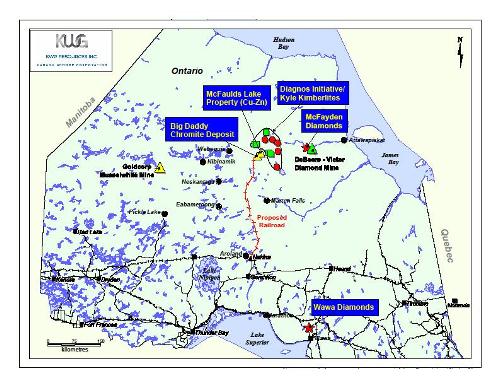
The isolated Ring of Fire mining camp, located in the James Bay lowlands of Ontario’s far north, is one of the most exciting and possibly the richest new Canadian mineral discovery made in over a generation. It has been compared to both the Sudbury Basin and the Abitibi Greenstone belt, which includes Timmins, Kirkland Lake, Noranda and Val d’Or.
Read more